Vodafone’s Organizational Structure
Create this exact chart in Organimi! Scroll below to see how.
Introduction
Vodafone — a portmanteau of voice, data, fone — is a publicly-traded British multinational telecommunications company with operations in Asia, Africa, Europe, and Oceania.
As of November 2021, the company operates networks and provides services to both consumer and business clients in 22 countries, with partner networks in a further 48 countries. Through its Vodafone Global Enterprise division, the company provides IT services to corporate clients in 150 countries.
Brief History of Vodafone
Vodafone can trace its roots back to 1981 with the founding of the Racal Strategic Radio Ltd subsidiary of Racal Electronics, the UK’s largest maker of military radio technology. This eventually evolved into Racal-Vodafone in 1985. In 1986, Vodafone became a brand under the ownership of Racal.
On 16 September 1991, Racal Telecom was demerged from Racal Electronics as Vodafone Group. On 19 November 1996, Vodafone purchased Peoples Phone, a 181-store chain whose customers were mostly using Vodafone’s network, for £77 million. In January 1997, the company introduced its famous Speechmark logo, and in September 1999, Vodafone merged its U.S. wireless assets with those of Bell Atlantic Corp to form Verizon Wireless.
In February 2000, Vodafone acquired German industry giant Mannesmann for £112 billion which was at the time the world’s largest-ever corporate merger. Throughout the 2000s, the company underwent a series of mergers and acquisitions and eventually sold off its 45% stake in Verizon Wireless to Verizon Communications for US$130 billion in 2013 and dedicated a chunk of proceeds from this sale to improving network infrastructure in Europe and emerging markets.
More recently, the company pulled out of the Diem Association, the governing council for the Facebook-created global digital currency initiative.
The Vodafone Foundation
Vodafone operates several charitable initiatives under its namesake charity, Vodafone Foundation. This supports and initiates projects which use mobile technology to benefit the vulnerable under the slogan “Connecting for Good”. The foundation’s charitable initiatives include:
- DreamLab, a mobile app developed to research COVID-19, cancer, and other diseases
- PERMS, a system that allows physicians to remotely make patient observations
- Safe Taxi System, technology that taxi drivers can use to alert police
Vodafone’s Global Leadership Team
Vodafone’s global operations are overseen by the Vodafone Executive Committee. The committee is responsible for the implementation and delivery of Vodafone’s strategy as agreed by the Vodafone Board, and for all aspects of operational management.
Nick Read is the current Chief Executive of Vodafone and he heads both the company’s Executive Committee and Board of Directors.
Also on the Executive Committee are several C-level officials who are responsible for different functional groups — for example, finance, legal, corporate affairs, and technology — and geographical locations where Vodafone operates, such as the UK, Germany, Spain, Italy, and South Africa (where Vodafone is known as Vodacom). The CEO of Vodafone Business also sits on the Executive Committee.
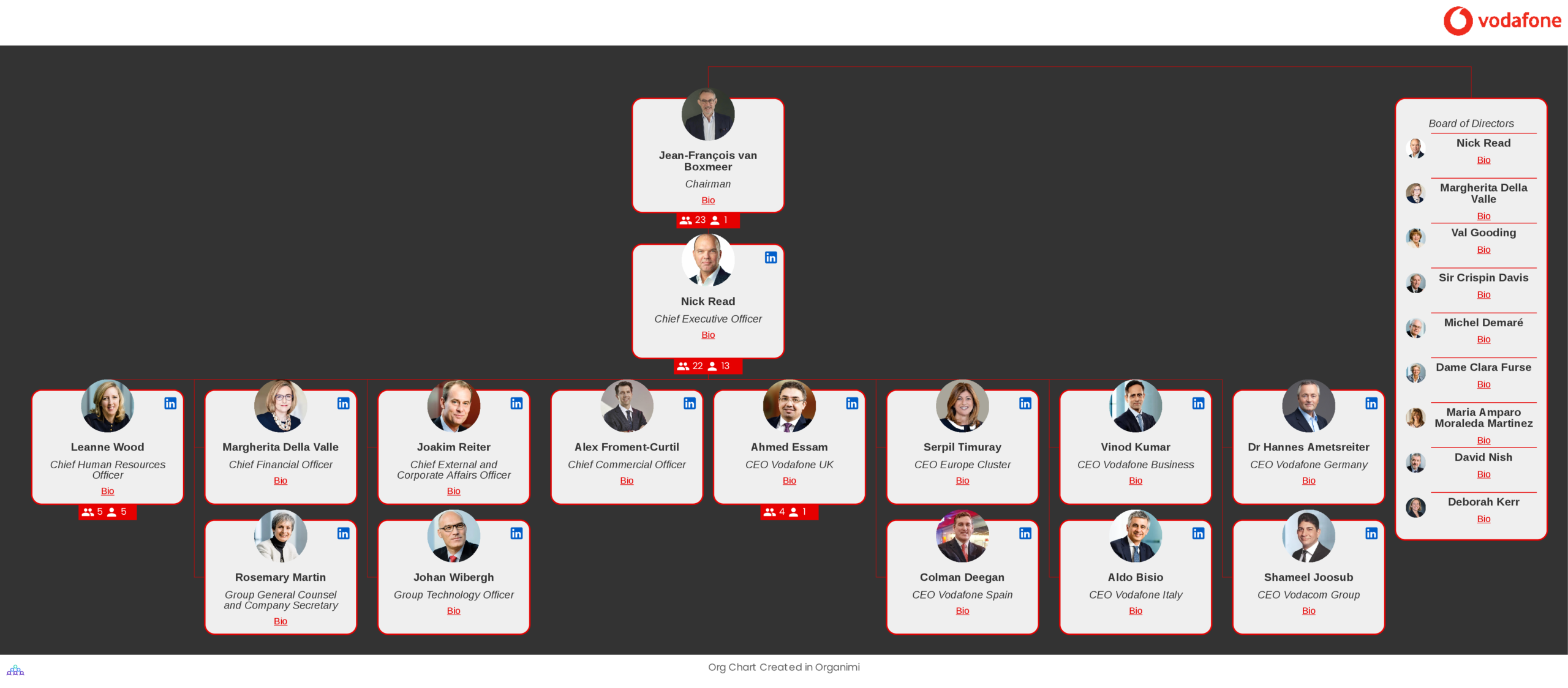
Executive Committee members overseeing the various geographical subsidiaries of Vodafone are CEOs and oversee their own national teams of high-level regional executives.
The CEO of Vodafone UK Ahmed Essam, for example, is assisted by various regional Directors who are responsible for regional functional groups, such as UK Human Resources, UK Corporate Affairs, and UK Finance.
Vodafone’s Organizational Structure
Vodafone operates an organizational structure that’s divided into geographic groups.
A geographic org structure organizes people within an organization by their physical location. This creates specific divisions for each location where each acts as their own company with their own personnel for key business functions.
For example, a geographic division might have its own functional departments — marketing, HR, sales — that operate independently to achieve its own strategic vision independently from the parent organization.
In essence, geographic organizational structures provide local divisions with the ability to do this by giving them the autonomy to respond to local market conditions while still following overarching business policy. This type of structure makes sense in large global businesses like Vodafone that serve many diverse markets.
Learn more about organizational charts:
If you want to learn more about org structures and the important role that they play in organizations like Vodafone, here are some resources that you can start with:
Create this chart in Organimi!
You can download the CSV file of Vodafone’s org structure, import it into Organimi and start editing this chart right away! Here’s how:
- From your dashboard, select Data Import.
- Click the CSV tile.
- Click +Upload Your File.
- Select an Excel file from your device.
- In the Organization field, click the down arrow to select an organization.
- Click Create a New Chart
- Click Next and select: Organization Chart
- Select the auto-build tool to automatically build your chart.
- Voila!
Download CSV file: Vodafone (26.98 KB)
Vodafone (26.98 KB)
Build better org charts with
Organimi.
A powerful, cloud-based platform that helps you create, connect, and collaborate with your colleagues wherever they work.